Tags: diffie-hellman
Rating:
> Difficulty : Intro
> [Source files](https://github.com/Phreaks-2600/PwnMeCTF-2025-quals/blob/main/Crypto/EasyDiffy/attachments/easydiffy.zip)
> Description : I managed to generate strong parameters for our diffie-hellman key exchange, i think my message is now safe.
> Author : wepfen (me ofc)
## TL;DR
- notice that $ g \equiv p-1 \equiv -1 \mod p $
- And when this happens, modular arithmetic tell us that $g^{k} \equiv (-1)^{k} \mod p$ which is either `1` or `-1`
- So the shared key is actually `g-1`, decrypt the flag with it
## Introduction
For this challenge we have a python script generating diffie hellman parameters and use the shared secret sha256 hash as a AES key to encrypt the flag.
I made this challenge so everyone can solve a challenge and have its shot of dopamine <3.
## Code analysis
Here's the python script.
```python
from Crypto.Util.number import getPrime, long_to_bytes
from Crypto.Util.Padding import pad, unpad
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from hashlib import sha256
import os
# generating strong parameters
flag = b"REDACTED"
p = getPrime(1536)
g = p-1
a = getPrime(1536)
b = getPrime(1536)
A = pow(g, a, p)
B = pow(g, b, p)
assert pow(A, b, p) == pow(B, a, p)
C = pow(B, a, p)
# Encrypting my message
key = long_to_bytes(C)
key = sha256(key).digest()[:16]
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_ECB)
ciphertext = cipher.encrypt(pad(flag, AES.block_size))
print(f"{p = }")
print(f"{g = }")
print("ciphertext =", ciphertext.hex())
```
And the output :
```python
p = 1740527743356518530873219004517954317742405916450945010211514630307030225825627940655848700898186119703288416676610512180281414181211686282526701502342109420226095690170506537523420657033019751819646839624557146950127906808859045989204720555752289247833349649020285507405445896768256093961814925065500513967524214087124440421275882981975756344900858314408284866222751684730112931487043308502610244878601557822285922054548064505819094588752116864763643689272130951
g = 1740527743356518530873219004517954317742405916450945010211514630307030225825627940655848700898186119703288416676610512180281414181211686282526701502342109420226095690170506537523420657033019751819646839624557146950127906808859045989204720555752289247833349649020285507405445896768256093961814925065500513967524214087124440421275882981975756344900858314408284866222751684730112931487043308502610244878601557822285922054548064505819094588752116864763643689272130950
ciphertext = f2803af955eebc0b24cf872f3c9e3c1fdd072c6da1202fe3c7250fd1058c0bc810b052cf99ebfe424ce82dc31a3ba94f
```
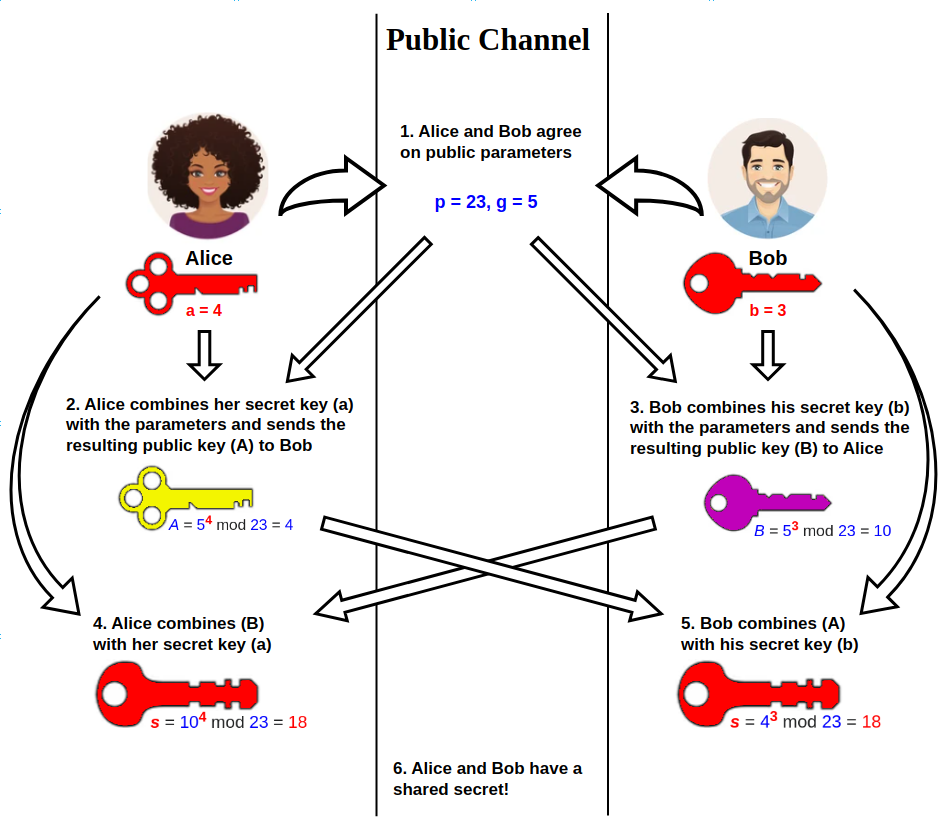
### Diffie Hellman reminder
Before reading the code, here's a quick recap of diffie hellman key exchange.
We got two person Alice and Bob who want to talk securely by encrypting their message with the same key. But they can't scream this key in front of everyone, because some eavesdroppers can steal this key to decrypt their conversation.
So instead, they exchange the key using mathematics.
Two public variables are selected and shared by Alice and Bob : `g` and `p`. `p` is a prime number and `g` is used to generate public keys.
Then Alice select a random number `a` modulo p, and compute it's public key `A` using `g` : $$A \equiv g^{a} \mod p$$
Then Bob does the same with it's private key `b` and send its public key `B` to Alice and receive Alice's public key.
Then they compute the shared secret `s` that will be the symmectric key to encrypt their communication :
$$ s \equiv A^{b} \equiv (g^{a})^{b} \equiv g^{ab}\mod p $$
$$ s \equiv B^{a} \equiv (g^{b})^{a} \equiv g^{ba}\mod p $$
### Actually reading the code
1. First a prime `p` is randomly generated and the generator `g` is equal to $p-1$
```python
p = getPrime(1536)
g = p-1
```
> A generator is, as his name suggest, used to generate a group of number by computing $g^{k} \mod p$. So if wrongly chosen, the group of number can be small and so it can compromise the robustness of the key exchange.
2. The private keys `a` and `b` are randomly chosen
```python
a = getPrime(1536)
b = getPrime(1536)
```
3. The public keys `A` and `B` are computed using the generator and the private keys
```python
A = pow(g, a, p)
B = pow(g, b, p)
```
4. The shared secret is computed
```python
assert pow(A, b, p) == pow(B, a, p)
C = pow(B, a, p)
```
5. Finally the shared secret is used as a key and the flag is encrypted with it
```python
key = long_to_bytes(C)
key = sha256(key).digest()[:16]
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_ECB)
ciphertext = cipher.encrypt(pad(flag, AES.block_size))
```
One may think it is a classic diffie hellman key exchange but by quickly looking at the [DHKE wiki page](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diffie%E2%80%93Hellman_key_exchange), we can understand that the chosen generator is uncommon.
Knowing a little bit of modular arithmetic (or just testing out the code), we can figure out that using $g = p-1$ makes every power of g equal to 1 or -1 mod p.
So, the public keys A and B, which are a power of `g`,are either 1 or -1 :
$$ g \equiv p-1 \mod p $$
$$ g \equiv -1 \mod p $$
$$ (-1)^{k} \equiv \pm 1 \mod p$$
It is equal to 1 if `k` is even.
And it is equal to 1 if `k` is odd.
$$
(-1)^k=\begin{cases}
-1 & k=\text{odd} \\
1 & k=\text{even }
\end{cases}
$$
But as the private keys are prime numbers, they are odd :
$$ g^{a} \equiv g^{b} \equiv -1 \equiv p-1 \mod p $$
So the shared secert is actually $p-1$.
And a topic about this : https://crypto.stackexchange.com/questions/77868/for-diffie-hellman-why-is-a-g-value-of-p%e2%88%921-not-a-suitable-choice.
## Solving
As we stated that the private key is p-1, we can reuse the g from the output.txt as the private key.
```python
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.Padding import unpad
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes
from hashlib import sha256
p = 1740527743356518530873219004517954317742405916450945010211514630307030225825627940655848700898186119703288416676610512180281414181211686282526701502342109420226095690170506537523420657033019751819646839624557146950127906808859045989204720555752289247833349649020285507405445896768256093961814925065500513967524214087124440421275882981975756344900858314408284866222751684730112931487043308502610244878601557822285922054548064505819094588752116864763643689272130951
ciphertext = bytes.fromhex("f2803af955eebc0b24cf872f3c9e3c1fdd072c6da1202fe3c7250fd1058c0bc810b052cf99ebfe424ce82dc31a3ba94f")
shared_secret = p - 1
key = long_to_bytes(shared_secret)
key = sha256(key).digest()[:16]
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_ECB)
message = unpad(cipher.decrypt(ciphertext), 16)
print(message)
```
FLAG : `PWNME{411_my_h0m13s_h4t35_sm411_Gs}`